The post-16 education and skills white paper reiterates what the Office for Students’ (OfS) recent consultation on the future of the Teaching Excellence Framework (TEF) had already made quite clear: there is a strong political will to introduce a regulatory framework for HE that imposes meaningful consequences on providers whose provision is judged as being of low quality.
While there is much that could be said about the extent to which TEF is a valid way of measuring quality or teaching excellence, we will focus on the potential unintended consequences of OfS’s proposals for the future of TEF.
Regardless of one’s views of the TEF in general, it is relatively uncontroversial to suggest that TEF 2023 was a material improvement on its predecessor. In an analysis of the outcomes from the 2017 TEF exercise, it was clear that a huge volume of work had gone into establishing a ranking of providers which was far too closely correlated with the characteristics of their student body.
Speaking plainly, the optimal strategy for achieving Gold in 2017 was to avoid recruiting too many students from socially and economically disadvantaged backgrounds. In 2017, the 20 providers with the fewest FSM students had no Bronze awards, while the 20 with the highest failed to have any Gold awards associated with their provision.
Following the changes introduced in the next round of TEF assessments, while there still appears to be a correlation between student characteristics and TEF outcomes, the relationship is not as strong as it was in 2017. Here we have mapped the distribution of TEF 2023 Gold, Silver and Bronze ratings for providers with the lowest (Table 1) and highest (Table 2) proportions of students who have received free school meals (FSM), for TEF 2023.
In TEF 2023, the link between student characteristics and TEF outcome was less pronounced. This is a genuine improvement, and one we should ensure is not lost under the new proposals for TEF.
Reconfiguring the conception of quality
The current TEF consultation proposes radical changes, not least of which is the integration of the regulator’s assessment of compliance with the B conditions of registration which deal with academic quality.
At present, TEF differentiates between different levels of quality that are all deemed to be above minimum standards – built upon the premise that the UK higher education sector is, on average, “very high quality” in an international context – and operates in parallel with the OfS’s approach to ensuring compliance with minimum standards. The proposal to merge these two aspects of regulation is being posited as a way of reducing regulatory burden.
At the same time, the OfS – with strong ministerial support – is making clear that it wants to ensure there are regulatory consequences associated with provision that fails to meet their thresholds. And this is where things become more contentious.
Under the current framework, a provider is technically not eligible to participate in TEF if it is judged by the OfS to fall foul of minimum quality expectations. Consequently, TEF ratings of Bronze, Silver and Gold are taken to correspond with High Quality, Very High Quality and Outstanding provision, respectively. While a fourth category, Requires Improvement, was introduced for 2023, vanishingly few providers were given this rating.
Benchmarked data on the publicly available TEF dashboard in 2023 were deemed to contribute no more than 50 per cent of the weight in each provider’s aspect outcomes. Crucially, data that was broadly in line with benchmark was deemed – as a starting hypothesis, if you will – to be consistent with a Silver rating: again, reinforcing the message that the UK HE sector is “Very High Quality” on the international stage.
Remember this, as we journey into the contrasts with proposals for the new TEF.
Under the proposed reforms, OfS has signalled that providers failing to be of sufficient quality would be subject to regulatory consequences. Such consequences could span from enhanced monitoring to – in extremis – deregistration; such processes and penalties would be led by OfS. We have also received the clear indication that the government may wish to withdraw permission to grow and receive inflation-linked fee increases with quality outcomes. In other words, providers who fail to achieve a certain rating in TEF may experience student number caps and fee freezes.
These are by no means minor inconveniences for any provider, and so one might reasonably expect that the threshold for implementing such penalties would be set rather high – from the perspectives both of the proportion of the sector that would, in a healthy system, be subject to regulatory action or governmental restriction at any one time, and the operational capacity of the OfS properly to follow through and follow up on the providers that require regulatory intervention. On the contrary, however, it is being proposed that both Requires Improvement- and Bronze-rated providers would be treated as inadequate in quality terms.
While a provider rated as Requires Improvement might expect additional intervention from the regulator, it seems less obvious why a provider rated Bronze – which was previously defined as a High Quality provider – should expect to receive enhanced regulatory scrutiny and/or restrictions on their operation.
It’s worse than we thought
As the sector regulator, OfS absolutely ought to be working to identify areas of non-compliance and inadequate quality. The question is whether these new proposals achieve that aim.
This proposal amounts to OfS making a fundamental change to the way it conceptualises the very notion of quality and teaching excellence, moving from a general assumption of high quality across the sector to the presumption that there is low quality at a scale hitherto unimagined. While the potential consequences of these proposed reforms are important at the level of an individual provider, and for student and prospective students’ perceptions, it is equally important to ask what they mean for the HE sector as a whole.
Figure 1 illustrates the way in which the ratings of quality across our sector might change, should the current proposals be implemented. This first forecast is based upon the OfS’s proposal that overall provider ratings will be defined by the lowest of their two aspect ratings, and shows the profile of overall ratings in 2023 had this methodology been applied then.
There are some important points to note regarding our methodology for generating this forecast. First, as we mentioned above, OfS has indicated an intention to base a provider’s overall rating on the lowest of the two assessed aspects: Student Experience and Student Outcomes. In TEF 2023, providers with mixed aspects, such as Bronze for one and Silver for another, may still have been judged as Silver overall, based on the TEF panel’s overall assessment of the evidence submitted. Under the new framework, this would not be possible, and such a provider would be rated Bronze by default. In addition, we are of course assuming that there has been no shift in metrics across the sector since the last TEF, and so these figures need to be taken as indicative and not definitive.
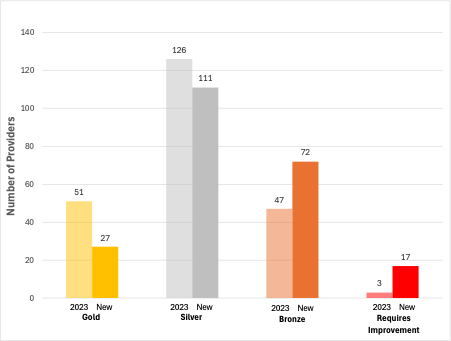
Figure 1: Comparison of predicted future TEF outcomes compared with TEF 2023 actual outcomes
There are two startling points to highlight:
- The effect of this proposed TEF reform is to drive a downward shift in the apparent quality of English higher education, with a halving of the number of providers rated as Outstanding/Gold, and almost six times the number of providers rated as Requires Improvement.
- The combined number of Bronze and Requires Improvement Providers would increase from 50 to 89. Taken together with the proposal to reframe Bronze as being of insufficient quality, OfS could be subjecting nearly 40 per cent of the sector to special regulatory measures.
In short, the current proposals risk serious destabilisation of our sector, and we argue could end up making the very concept of quality in education less, not more, clear for students.
Analysis by provider type
Further analysis of this shift reveals that these changes would have an impact across all types of provider. Figures 2a and 2b show the distribution of TEF ratings for the 2023 and projected future TEF exercises, where we see high, medium and low tariff providers, as well as specialist institutions, equally impacted. For the 23 high tariff providers in particular, the changes would see four providers fall into the enhanced regulatory space of Bronze ratings, whereas none were rated less than Silver in the previous exercise. For specialist providers, of the current 42 with 2023 TEF ratings, five would be judged as Requires Improvement, whereas none received this rating in 2023.
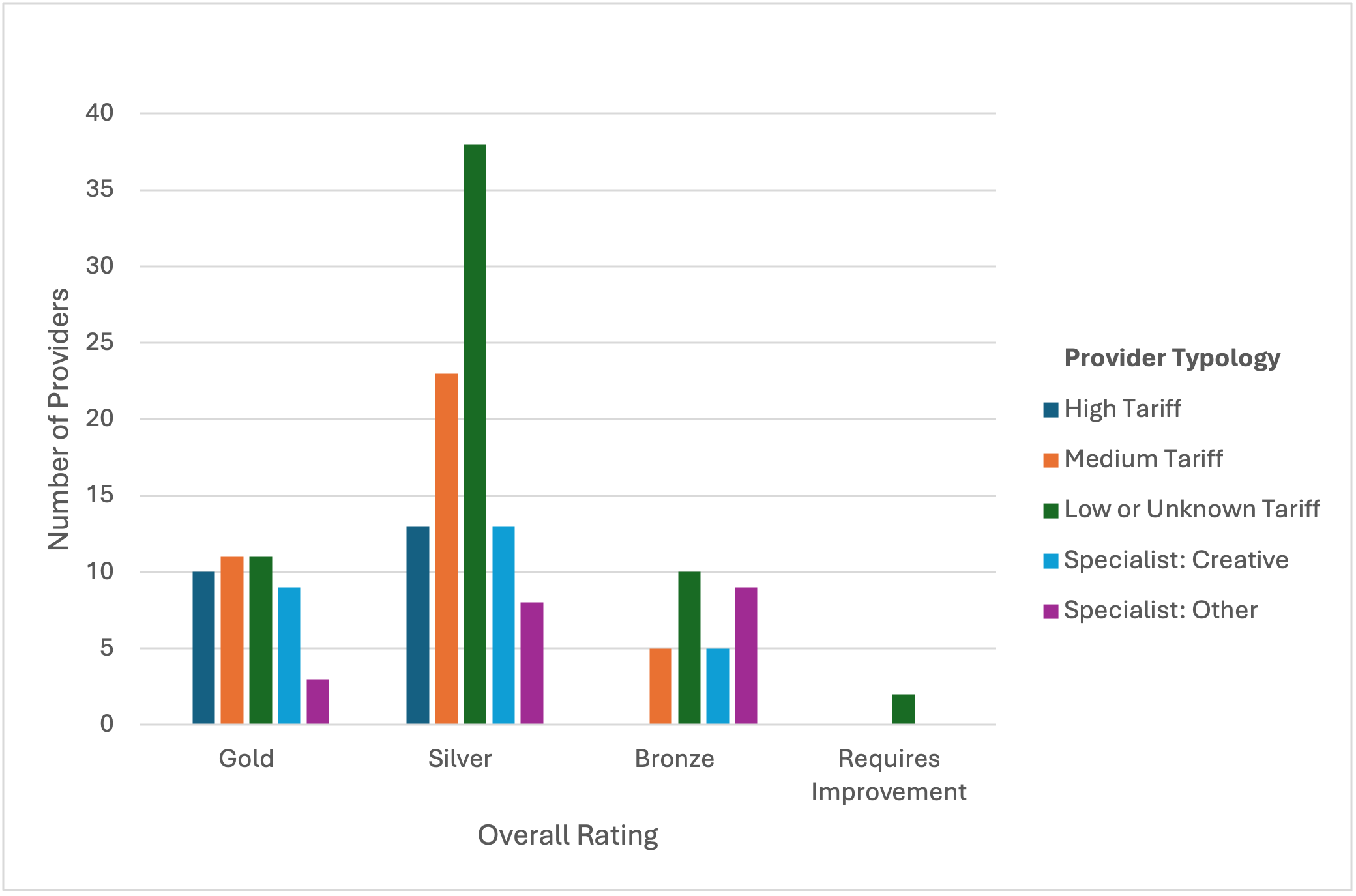
Figure 2a: Distribution of TEF 2023 ratings by provider type
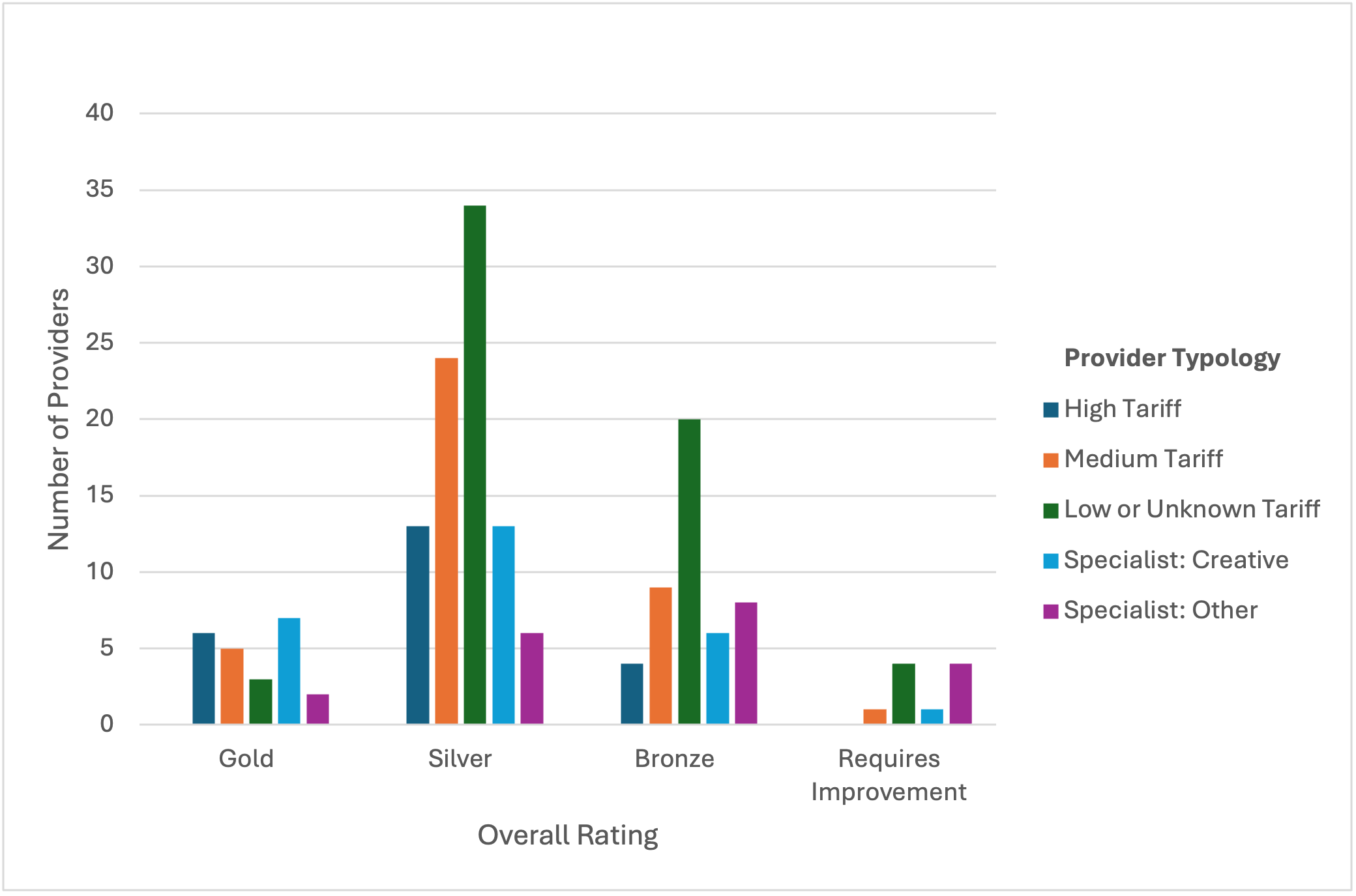
Figure 2b: Predicted distribution of future TEF ratings by provider type
Such radical movement in OfS’s overall perception of quality in the sector requires explanation. Either the regulator believes that the current set of TEF ratings were overly generous and the sector is in far worse health than we have assumed (and, indeed, than we have been advising students via current TEF ratings), or else the very nature of what is considered to be high quality education has shifted so significantly that the way we rate providers requires fundamental reform. While the former seems very unlikely, the latter requires a far more robust explanation than has been provided in the current consultation.
We choose to assume that OfS does not, in fact, believe that the quality of education in English HE has fallen off a cliff edge since 2023, and also that it is not intentionally seeking to radically redefine the concept of high quality education. Rather, in pursuit of a regulatory framework that does carry with it material consequences for failing to meet a robust set of minimum standards, we suggest that perhaps the current proposals have missed an opportunity to make more radical changes to the TEF rating system itself.
We believe there is another approach that would help the OfS to deliver its intended aim, without destabilising the entire sector and triggering what would appear to be an unmanageable volume of regulatory interventions levelled at nearly 40 per cent of providers.
Benchmarks, thresholds, and quality
In all previous iterations of TEF, OfS has made clear that both metrics and wider evidence brought forward in provider and student submissions are key to arriving at judgements of student experience and outcomes. However, the use of metrics has very much been at the heart of the framework.
Specifically, the OfS has gone to great lengths to provide metrics that allow providers to see how they perform against benchmarks that are tailored to their specific student cohorts. These benchmarks sit alongside the B3 minimum thresholds for key metrics, which OfS expects all providers to achieve. For the most part, providers eligible to enter TEF would have all metrics sitting above these thresholds, leaving the judgement of Gold, Silver and Bronze as a matter of the distance from the provider’s own benchmark.
The methodology employed in TEF has also been quite simple to understand at a conceptual level:
- A provider with metrics consistently 2.5 per cent or more above benchmark might be rated as Gold/Outstanding;
- A provider whose metrics are consistently within ±2.5 per cent of their benchmarks, would be likely assessed as Silver/Very High Quality;
- Providers who are consistently 2.5 per cent or more below their benchmark would be Bronze/High Quality or Requires Improvement.
There is no stated numerical threshold that is consistent with the boundary between Bronze and Requires Improvement – a matter of holistic panel judgement, including but not limited to how far beyond -2.5 per cent of benchmark a provider’s data sits.
It is worth noting here that in the current TEF, Bronze ratings (somewhat confusingly) could only be conferred for providers who could also demonstrate some elements of Silver/Very High Quality provision. Under the new TEF proposals, this requirement would be dropped.
The challenge we see here is with the definition of Bronze being >2.5 per cent below benchmark; the issue is best illustrated with an example of two hypothetical Bronze providers:
Let’s assume both Provider A and B have received a Bronze rating in TEF, because their metrics were consistently more than 2.5 per cent below benchmark, and their written submissions and context did not provide any basis on which a higher rating ought to be awarded. For simplicity, let’s pick a single metric, progression into graduate employment, and assume that the benchmark for these two providers happens to be the same, at 78 per cent.
In this example, Provider A obtained its Bronze rating with a progression figure of 75 per cent, which is 3 per cent below its benchmark. Provider B, on the other hand, had a Progression figure of 63 per cent. While this is a full 12 percentage points worse than Provider A, it is nonetheless still 2 per cent above the minimum threshold specified by OfS, which is 60 per cent, and so it was not rated as Requires Improvement.
Considering this example, it seems reasonable to conclude that Provider A is doing a far better job of supporting a comparable cohort of students into graduate employment than Provider B, but under the new TEF proposals, both are judged as being Bronze, and would be subject to the same regulatory penalties proposed in the consultation. From a prospective student’s perspective, it is hard to see what value these ratings would carry, given they conceal very large differences in the actual performance of the providers.
On the assumption that the Requires Improvement category would be retained for providers with more serious challenges – such as being below minimum thresholds in several areas – the obvious problem is that Bronze as a category in the current proposal is simply being stretched so far, it will lose any useful meaning. In short, the new Bronze category is too blunt a tool.
An alternative – meet Meets Minimum Requirements
As a practical solution, we recommend that OfS considers a fifth category, sitting between Bronze and Requires Improvement: a category of Meets Minimum Requirements.
This approach would have two advantages. First, it would allow the continued use of Bronze, Silver and Gold in such a way that the terms retain their commonly understood meanings; a Bronze award, in common parlance, is not a mark of failure. Second, it would allow OfS to distinguish providers who, while below our benchmark for Very High Quality, are still within a reasonable distance of their benchmark such that a judgement of High Quality remains appropriate, from those whose gap to benchmark is striking and could indicate a case for regulatory intervention.
The judgement of Meets Minimum Requirements would mean the provider’s outcomes do not fall below the absolute minimum thresholds set by the regulator, but equally are too far from their benchmark to be awarded a quality kitemark of at least a Bronze TEF rating. The new category would reasonably be subject to increased regulatory surveillance, given the borderline risk of thus rated providers failing to meet minimum standards in future.
We argue that such a model would be far more meaningful to students and other stakeholders. TEF ratings of Bronze, Silver and Gold would continue to represent an active recognition of High, Very High, and Outstanding quality, respectively. In addition, providers meeting minimum requirements (but not having earned a quality kitemark in the form of a TEF award) would be distinguishable from providers who would be subject to active intervention from the regulator, due to falling below the absolute minimum standards.
It would be a matter for government to consider whether providers deemed to be meeting minimum requirements should receive inflation-linked uplifts in fees, and should be permitted to grow; indeed, one constructive use of the increased grading nuance we propose here could be that providers who meet minimum requirements are subject to student number caps until they can demonstrate capability to grow safely by improving to the point of earning at least a Bronze TEF award. Such a measure would seem proportionately protective of the student interest, while still differentiating those providers from providers who are actively breaching their conditions of registration and would be subject to direct regulatory intervention.
Modelling the impact
To model how this proposed approach might impact overall outcomes in a future TEF, we have, in the exercise that follows, used TEF 2023 dashboard data and retained the statistical definitions of Gold (>2.5 per cent above benchmark) and Silver (±2.5% of benchmark) from the current TEF. We have modelled a proposed definition of Bronze as between 2.5-5 per cent below benchmark. Providers who Meet Minimum Requirements are defined as being within 5-10 per cent below benchmark, and Requires Improvement reflects metrics >10 per cent below benchmark.
For the sake of simplicity, we have taken the average distance from benchmark for all Student Experience and Student Outcomes metrics for each provider to categorise providers for each Aspect Rating. The outcome of our analysis is shown in Table A, and is contrasted in Table B with an equivalent analysis under OfS’s current proposals to redefine a four-category framework.
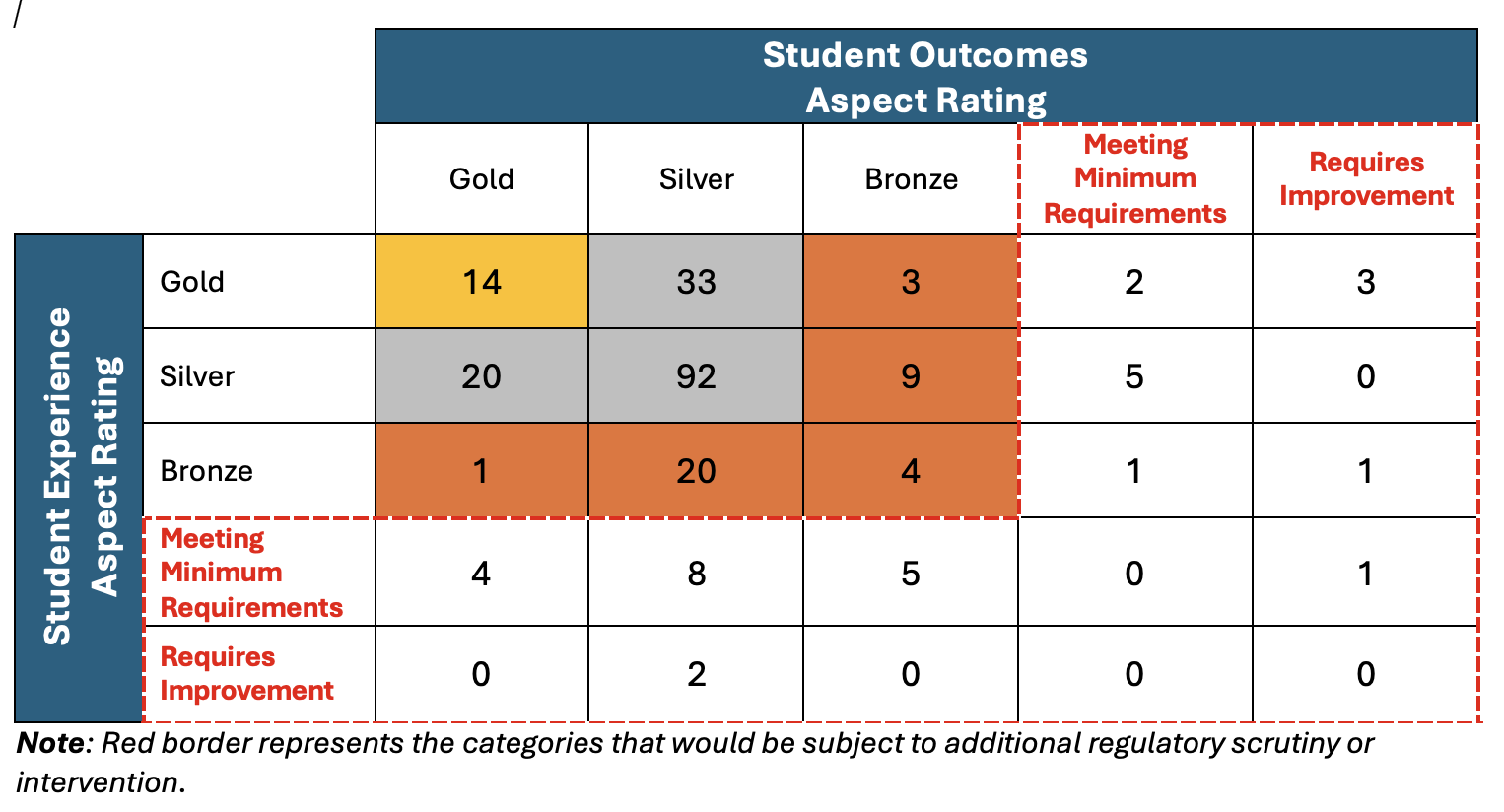
Table A. Distribution of aspect ratings according to a five-category TEF framework
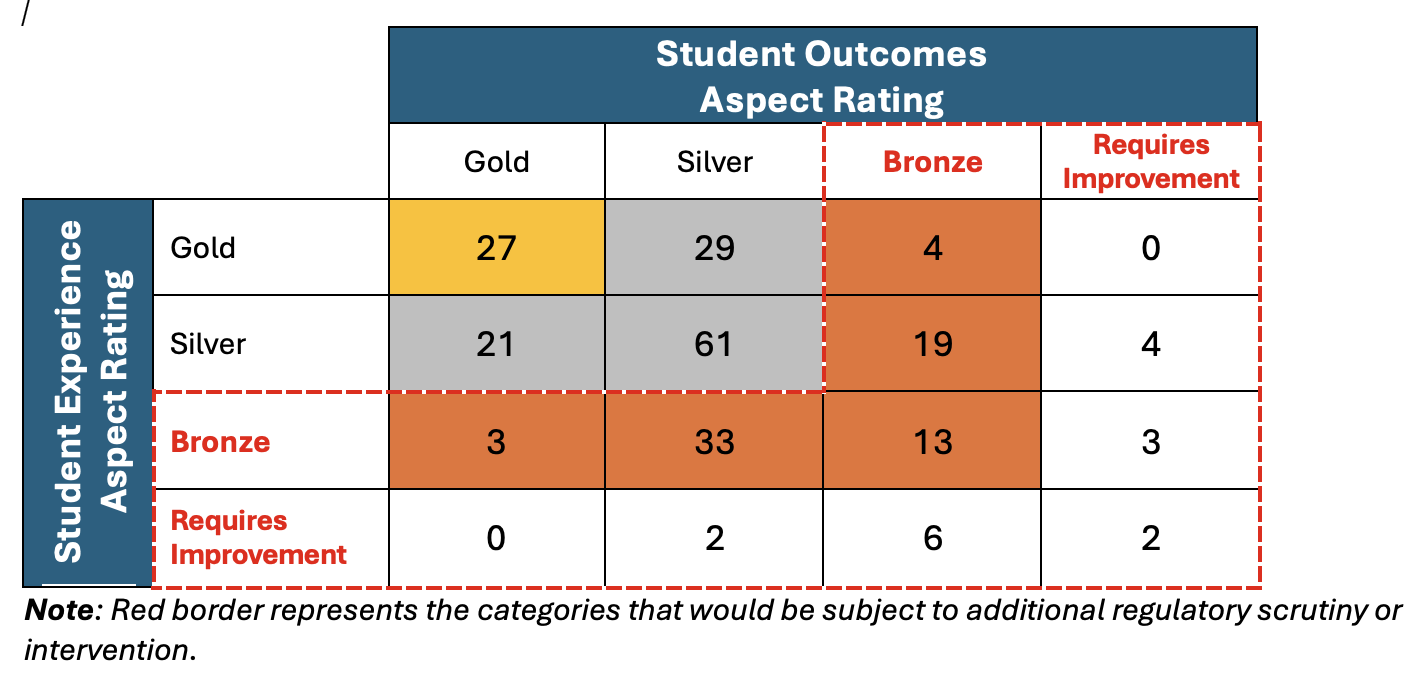
Table B. Distribution of aspect ratings according to OfS’s proposed four-category TEF framework
Following OfS’s proposal that a provider would be given an overall rating that reflects the lowest rating of the two aspects, our approach leads to a total of 32 providers falling into the Meets Minimum Requirements and Requires Improvement categories. This represents 14 per cent of providers, which is substantially fewer than the 39 per cent of providers who would be considered as not meeting high quality expectations under the current OfS proposals. It is also far closer to the 22 per cent of providers who were rated Bronze or Requires Improvement in TEF 2023.
We believe that our approach represents a far more valid and meaningful framework for assessing quality in the sector, while OfS’ current proposals risk sending a problematic message that, since 2023, quality across the sector has inexplicably and catastrophically declined. Adding granularity to the ratings system in this way will help OfS to focus its regulatory surveillance where it will likely be the most useful in targeting provision that is of potentially low quality.
Figure 4, below, illustrates the distribution of potential TEF outcomes based on OfS’s four category rating framework, contrasted with our proposed five categories. It is important to note that this modelling is based purely on metrics and benchmarks, and does not incorporate the final judgement of TEF panels, based on the narrative submissions providers submit.
This is particularly important because previous analysis has shown that many providers with metrics that were not significantly above benchmark, or not significantly at benchmark, were nonetheless awarded Gold or Silver ratings, respectively, and this would have been based on robust narrative submissions and other evidence submitted by providers. Equally, some providers with data that was broadly in line with benchmark were awarded Bronze ratings overall, as the further evidence submitted in the narrative statements failed to convince the panel of an overall picture of very high quality.
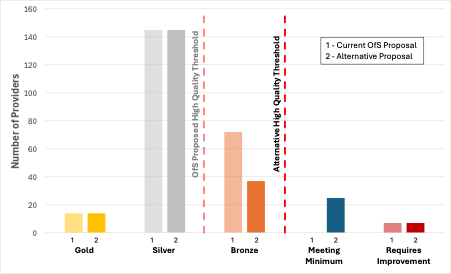
Figure 4: Predicted profile of provider ratings in a four- and five-category framework
The benefits of a five-category approach
First, the concept of a TEF award in the form of a Gold, Silver or Bronze rating retains its meaning for students and other stakeholders. Any of these three awards reflect something positive about a provider delivering beyond what we minimally expect.
Second, the pool of providers potentially falling into categories that would prompt enhanced scrutiny and potential regulatory intervention/governmental restrictions would drop to a level that would be a much fairer reflection of the actual quality of our sector. We simply do not believe it to be the case that anyone can be convinced that as much as 40 per cent of our sector is not of sufficiently high quality.
Third, referencing the socio-economic diversity data by 2023 TEF award in Tables 1 and 2, and the future TEF outcomes modelling in Figure 1, our proposal significantly reduces the risk that students who were previously eligible for free school meals (who form strong proportions of the cohorts of Bronze-rated providers) would be further disadvantaged by their HE environment being impoverished via fee freezes and student number caps. We argue that such potential measures should be reserved for the Requires Improvement, and, plausibly, Meets Minimum Requirements categories.
Fourth, by expanding the range of categories, OfS would be able to distinguish to between providers who are in fact meeting minimum expectations, but not delivering quality in experience or outcomes which would allow them to benefit from some of the freedoms proposed to be associated with TEF awards, and providers who are, in at least one of these areas, failing to meet even those minimum expectations.
To recap, the key features of our proposal are as follows:
- Retain Bronze, Silver and Gold in the TEF as ratings that reflect a positive judgement of High, Very High, and Outstanding quality, respectively.
- Introduce a new rating – Meets Minimum Requirements – that recognises providers who are delivering student experience and outcomes that are above regulatory minimum thresholds, but are too far from benchmarks to justify an active quality award in TEF. This category would be subject to increased OfS surveillance, given the borderline risk of provision falling below minimum standards in future.
- Retain Requires Improvement as a category that indicates a strong likelihood that regulatory intervention is required to address more serious performance issues.
- Continue to recognise Bronze ratings as a mark of High Quality, and position the threshold for additional regulatory restrictions or intervention such that these would apply only to providers rated as Meets Minimum Requirements or Requires Improvement.
Implementing this modest adaptation to the current TEF proposals would safeguard the deserved reputation of UK higher education for high-quality provision, while meeting the demand for a clear plan to secure improvements to quality and tackle pockets of poor quality.
The deadline for responding to OfS’ consultation on TEF and the integrated approach to quality is Thursday 11 December.