Drive along any motorway in September and you will see car after car full of duvets, pots and pans, and clothes as students head off to pastures new. I remember my own experience, crossing the Severn Bridge with the bedding on the front seat of my Fiesta muffling Oasis’ Definitely Maybe.
This stereotypical view of a literal journey into higher education isn’t the case for everyone, however. In fact, far more students live at home during their studies than you may think.
The UCAS application asks students about whether they intend to live at home. In 2024, 30 per cent of UK 18-year-olds said they planned to live at home during their studies – up from 25 per cent in 2019 and just 21 per cent in 2015.
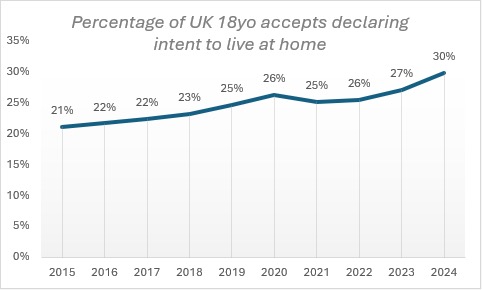
However, when we look beyond the headline numbers, over half of the most disadvantaged students (IMD Q1) live at home during their studies, compared to fewer than one in five of the least disadvantaged (IMD Q5). Regional distribution will have an impact here, particularly London.
Scottish students are more likely to live at home during their studies. On a recent visit to Edinburgh, all the students I met spoke with excitement about their plans to study at their chosen university within the city. By contrast, Welsh domiciled students are the least likely to live at home during their studies.
In London, 52 per cent of 18-year-olds progress to HE – with around half of those students staying in London, making it unsurprising that the capital sees the highest proportion of live at home students in England.
Cost of living pressures
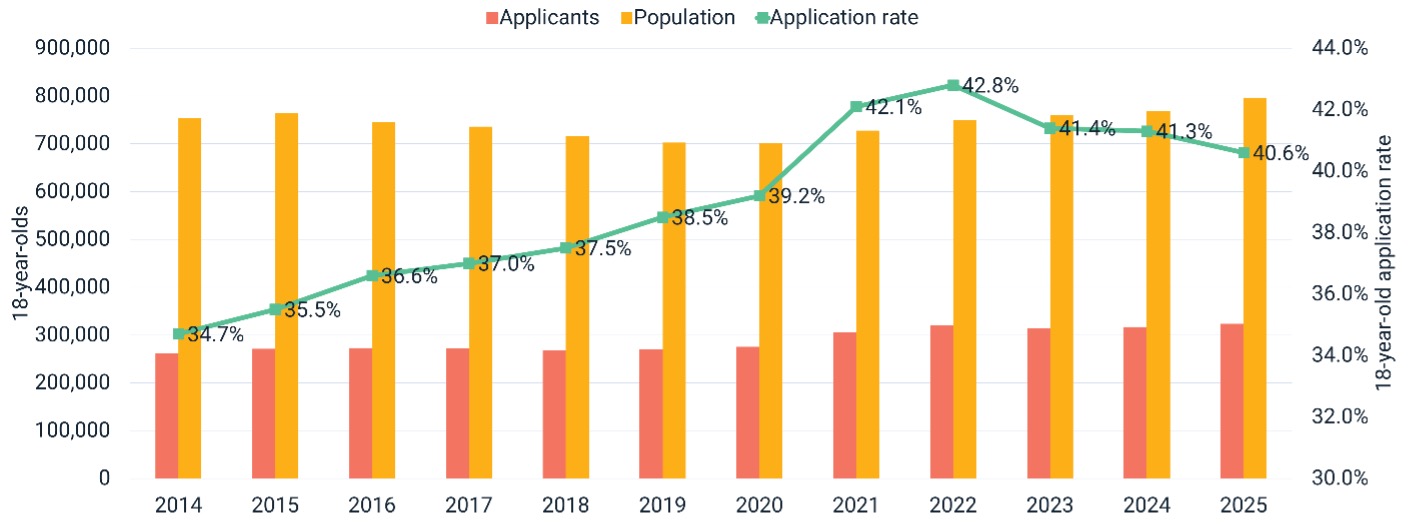
Cost of living is undoubtedly influencing student choice. At the January equal consideration deadline, UCAS saw a 2.1 per cent increase in the number of UK 18-year-old applicants – a record high. However, regular readers of Wonkhe will know this also represents a decline in the application rate – the proportion of the 18-year-old population applying to HE, and UCAS insight increasingly points to the cost of living playing a role.
Our latest survey insight suggests that 43 per cent of pre-applicants feel they are less likely to progress to HE due to cost-of-living pressures, up from 24 per cent in 2023 – although their commitment to going to university remains high.
Financial support is also of growing importance to students when it comes to deciding where to study. While finding the perfect course content was the most important factor when shortlisting universities (49 per cent), the financial support available while studying (such as a scholarship or bursary) was a close second (46 per cent). Specific cost-of-living support offered by universities was third (34 per cent).
The availability of support with the cost of living has risen in relative importance as a factor when shortlisting universities from 12th in 2022 to 3rd in 2024 – a significant shift, which suggests a change in student mindset. There have also been large changes in rank importance of “universities that are close to home” from 9th to 4th, “universities with low-cost accommodation” from 13th to 7th and “universities I can attend but still live with my parents” from 16th to 11th.
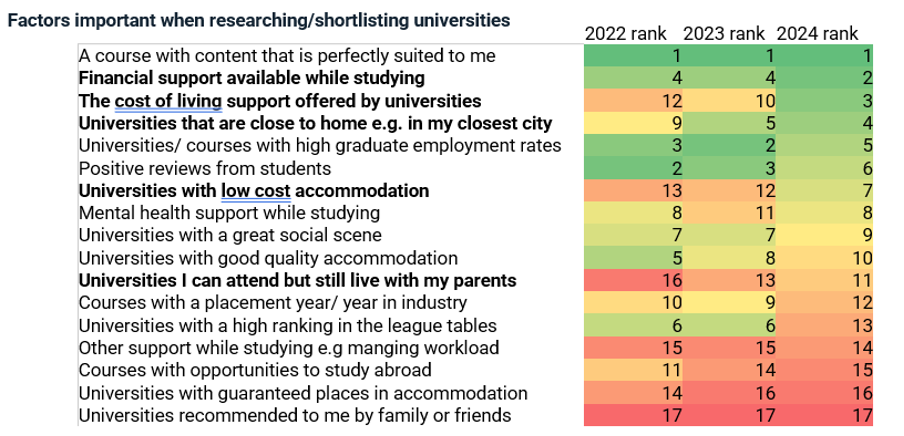
Source: Potential applicants for 2025 entry, 1,023 UK respondents, Dec 2024–Jan 2025
It isn’t just at the point of application where we see the cost of living impacting choice. In 2024, UCAS saw 43,000 students decline the place they were holding in favour of an alternative institution or subject – making this the largest group of students using Clearing.
This is not a spur of the moment decision, with 52 per cent having already decided to do this prior to receiving their results and a further one in five considering it based on their results.
When asked what drove their decision, 23 per cent told us they had a change in personal circumstances and 17 per cent wanted to live somewhere cheaper. We also know this impacts on all cohorts of students – 19 per cent of international students that don’t accept a university offer through UCAS tell us they have found a more attractive financial offer elsewhere.
However, the primary reason that students use Decline My Place is linked to the course, with 31 per cent changing their mind about the subject they wish to study.
Support measures
It’s clear that cost of living and financial support is a key factor influencing student choice and so we must ensure this information is easily accessible and understood by students.
Students tell us they’d like more practical information about student discounts, financial support packages or bursaries/scholarships. UCAS will shortly be launching a scholarships and bursary tool to promote these opportunities to students.
Around half of offer holders in 2024 recalled receiving information about cost of living support. This presents a timely opportunity for any university staff working in marketing, recruitment or admissions to ensure information about financial support is easy to find on their website, along with information about timetabling to help students understand how they may be able to balance work and study commitments.
There will be certain groups of students that are even more acutely impacted by cost of living challenges. Last cycle saw a record number of students in receipt of Free School Meals – 19.9 per cent – enter HE. Whilst it is only a small part of the puzzle, UCAS has removed the application fee for these students.
Cost of living pressures are likely to persist, with students continuing to assess the value of HE in this context. The sector should continue to highlight the benefits of university study as a vehicle for social mobility, along with the graduate premium – the higher earnings they typically earn compared to non-graduate peers. But we also need to make it clearer how HE of all forms remains accessible – from funds for travel to open days, to in study commuter breakfasts, hardship funds, cost of living support, and high-quality careers guidance to support graduate employability.
This article is published in association with UCAS. It forms part of our ongoing series on commuter students – you can read the whole series here.













‘Last cycle saw a record number of students in receipt of Free School Meals – 19.9 per cent – enter HE’
Where does this figure come from out of interest? The last DfE WPiHE release had the HE progression rate at 29 per cent for FSM students. The only 19.9 figure I could find was the disadvantage progression rate gap, which in 2022/23 was at its highest in a decade.